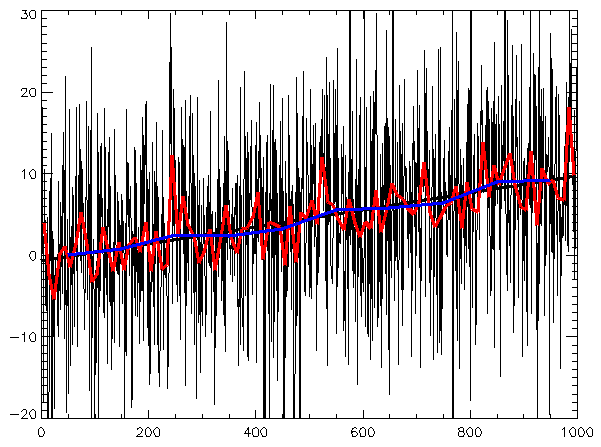
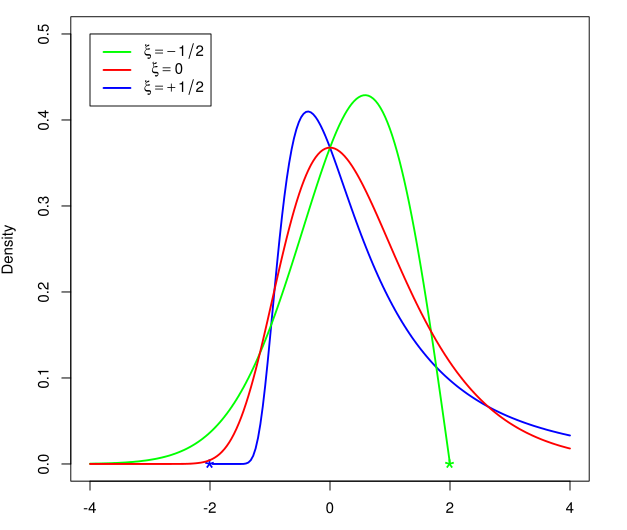
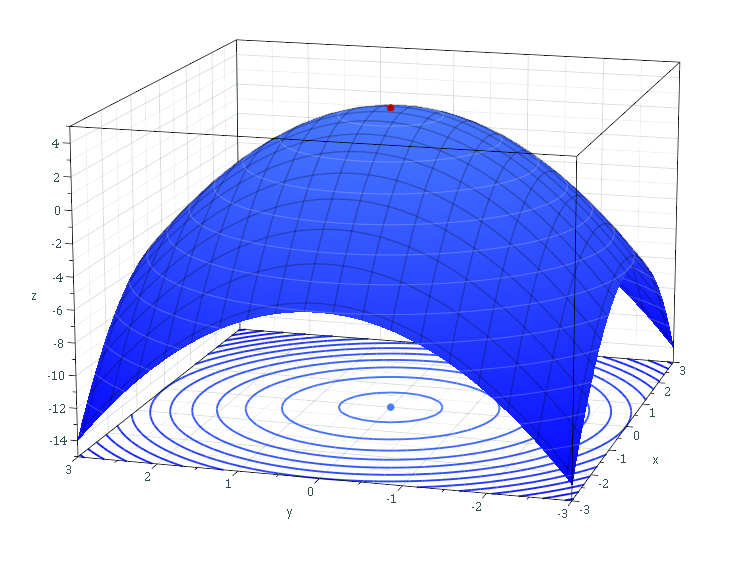
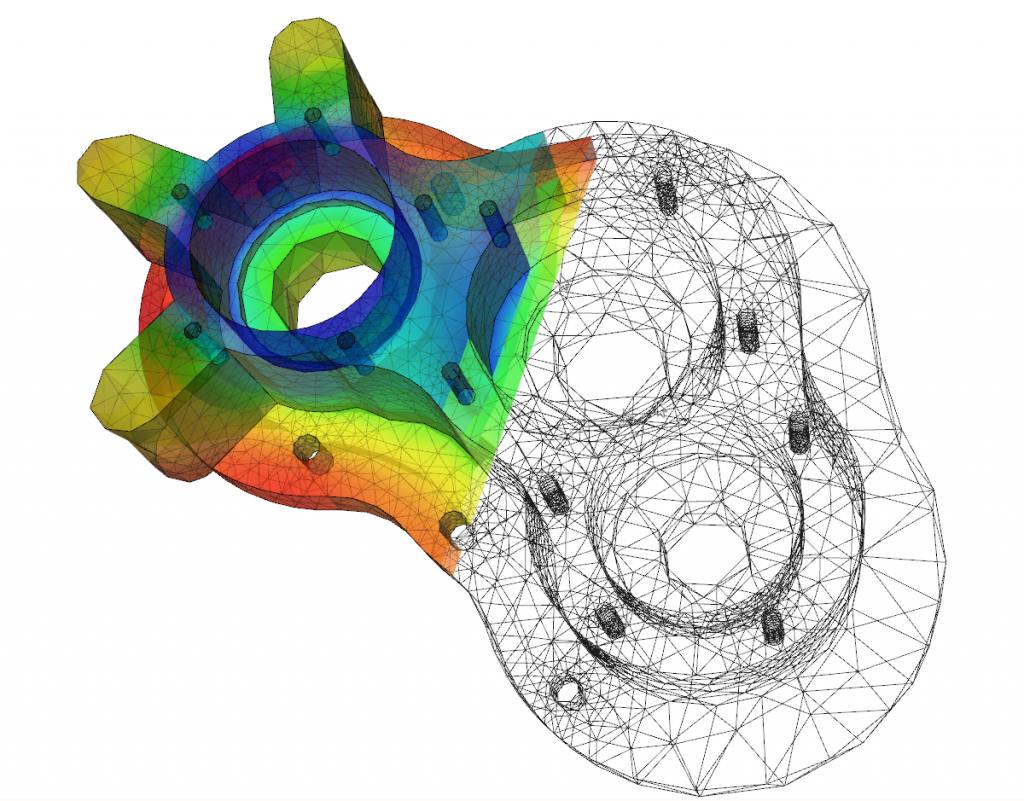
NM Dev is an object-oriented, high performance, extensively tested, and professionally documented programming library of mathematics that runs on S2. Having been developed since 2010, it is a large collection of numerical algorithms so coded such that they are solidly object-oriented, unified and testable. A user, who has little programming experience or mathematical sophistication, can easily create a solution for his or her complex engineering problem by quickly putting together classes.
SuanShu, now an open source project, has been replaced with NM Dev which has improved capability. NM Dev is also commercially supported. See our setup guide to get started using NM Dev on your local machine, or try it with our very own S2 IDE.
We have recently published a book that teaches math or numerical programming in Java using NM Dev/SuanShu. There are plenty of examples, which can be found in GitHub.
S2, an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for data science. Built using Java technology and NM Dev, it enables data scientists to write high performance code that runs on devices with a JVM. Compared to Python, it is much faster and is much easier to deploy. S2 is a one-stop shop of advanced analytics and data for engineers to quickly prototype computation models. See our available libraries here.
Features
Benchmarks
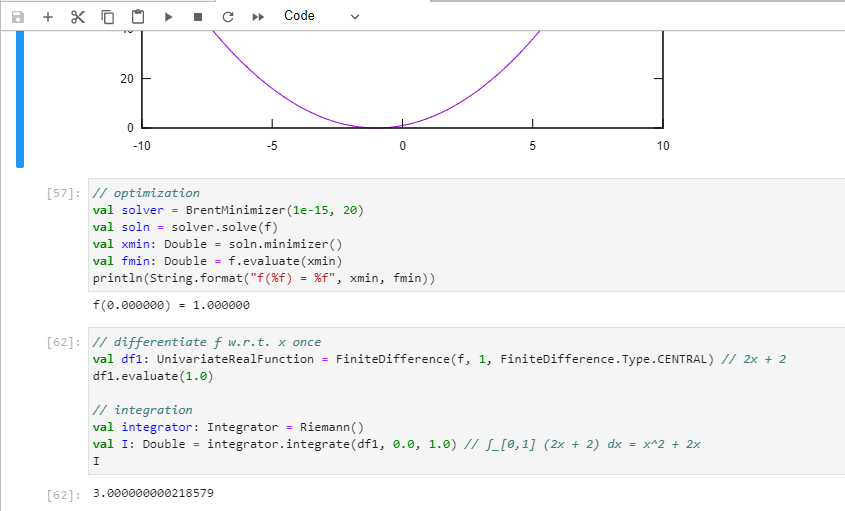
NM Dev is probably the fastest linear algebra library in Java!
NM Dev has a suite of high performance optimization algorithms.

We offer a limited trial for NM Dev, the Java numerical library.
Download here:
![]() nmdev-1.2.4.zip (13.8 MiB, 4,007 hits)
nmdev-1.2.4.zip (13.8 MiB, 4,007 hits)
We can further improve NM Dev to suit your needs by adding functions, improving speed and optimize it as per your requirements as a consulting project.
NM Dev distribution is deployed in NM’s repository. To let maven be aware of this repository, add the following repository definition to the pom.xml in the <repositories> section:
<repository>
<id>nm-repo</id>
<name>NM maven repository</name>
<url>https://repo.nm.dev/repository/maven-public/</url>
<layout>default</layout>
</repository>To use NM Dev, in the <dependencies> section, add:
<dependency>
<groupId>dev.nm</groupId>
<artifactId>nmdev</artifactId>
<version>1.2.4</version>
</dependency>Licensing
Community License
- BASIC
- OPTIM
- STATS
Academic License
- BASIC
- OPTIM
- STATS
Commercial License
- BASIC
- OPTIM
- STATS
- O/PDE
- EVT
Contributor License
- Customized
Hong Kong, China
Beijing, China
- 智速科技有限公司
- 北京大学
- 中国人民大学
Shanghai, China
- 上海简雍资产管理有限公司
- 中国科学院上海生命科学研究院
Shenzhen, China
Taiwan, China
- National Chiao Tung University
- National Taiwan University
Singapore
- Call Levels
- Robust Tech House
- Agency for Science Technology and Research
Indonesia
- BINUS UNIVERSITY INTERNATIONAL
Vietnam
- Saigon University
India
- Dynamic Levels
- NATIONAL ATMOSPHERIC RESEARCH LABORATORY, Government of India
- Supercomputer Education and Research Centre
- Computer Science, Indian Institute of Science
Switzerland
- Argentière Capital AG
Israel
- Tel Aviv University
Italy
- PricewaterhouseCoopers
- ERG Services SpA
Spain
- Universidad Carlos III de Madrid
Denmark
- Applied Crypto Aps
Norway
- Norges teknisk-naturvitenskapelige universitet
Sweden
- Uppsala University
Poland
- Jagiellonian University
- Politechnika Świętokrzyska
United Kingdom
- Cabestan Research
- Xenfin Capital Ltd
- University of York
- University of Birmingham
- University of Nottingham
- University of St Andrews
- Swansea University
Scotland, United Kingdom
- University of Strathclyde
California, USA
New York, USA
Massachusetts, USA
Florida, USA
- Parallax Quantitative Asset Management
Georgia, USA
Mexico
- Centro de Enseñanza Tecnica Industrial
Brasil
- Universidade de São Paulo
Hong Kong, China
Beijing, China
- 智速科技有限公司
- 北京大学
- 中国人民大学
Shanghai, China
- 上海简雍资产管理有限公司
- 中国科学院上海生命科学研究院
Shenzhen, China
Taiwan, China
- National Chiao Tung University
- National Taiwan University
Singapore
- Call Levels
- Robust Tech House
- Agency for Science Technology and Research
Indonesia
- BINUS UNIVERSITY INTERNATIONAL
Vietnam
- Saigon University
India
- Dynamic Levels
- NATIONAL ATMOSPHERIC RESEARCH LABORATORY, Government of India
- Supercomputer Education and Research Centre
- Computer Science, Indian Institute of Science
Switzerland
- Argentière Capital AG
Israel
- Tel Aviv University
Italy
- PricewaterhouseCoopers
- ERG Services SpA
Spain
- Universidad Carlos III de Madrid
Denmark
- Applied Crypto Aps
Norway
- Norges teknisk-naturvitenskapelige universitet
Sweden
- Uppsala University
Poland
- Jagiellonian University
- Politechnika Świętokrzyska
United Kingdom
- Xenfin Capital Ltd
- Xenfin Capital Ltd
- University of York
- University of Birmingham
- University of Nottingham
- University of St Andrews
- Swansea University
Scotland, United Kingdom
- University of Strathclyde
California, USA
New York, USA
Massachusetts, USA
Florida, USA
- Parallax Quantitative Asset Management
Georgia, USA
Mexico
- Centro de Enseñanza Tecnica Industrial
Brasil
- Universidade de São Paulo

This is a FREE, experimental version of the SuanShu library for the dot net environment. To download, register with us and login.
![]() suanshu.net-3.0.1.zip (13.1 MiB, 873 hits)
suanshu.net-3.0.1.zip (13.1 MiB, 873 hits)
You do not have permission to download this file.
For more information, see: